Abstract
Vancomycin is an antimicrobial widely used in hospitalized newborns (NB), with different dosing schedules that may or may not recommend the use of loading doses, depending on gestational age (GA), weight, and renal function.
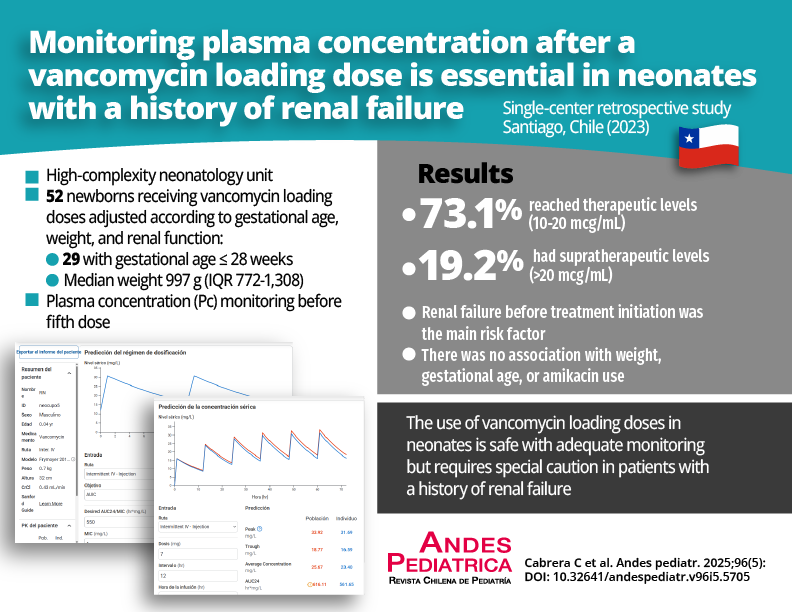
Objective: To evaluate the use of plasma levels after a vancomycin loading dose and its impact on achieving the target area under the curve/minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC/MIC) in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Patients and Method: Retrospective, descriptive, and observational study in NBs hospitalized between December 2022 and December 2023, in a high-complexity NICU. All NBs with empiric/targeted vancomycin indication were included, who received loading doses with baseline plasma concentration (Pc) monitoring, according to local protocol. Demographic and clinical data were recorded. Renal failure was considered when creatinine increased by 0.3 mg/dl in 48 hours and/or urinary output ≤ 1 ml/kg/day. The PrecisePK® software was used to estimate pharmacokinetic parameters and the AUC.
Results: 52 vancomycin Pc samples were analyzed, of which 73.1% reached optimal values between 10-20 mcg/ml, 19.2% Pc samples were supratherapeutic (> 20 mcg/ml), and 86% of patients achieved an AUC between 400- 600 mg/L. The main risk factor for supratherapeutic Pc was renal failure before treatment (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: This study indicates that the loading dose of vancomycin achieves optimal AUC in 86% of cases. It is recommended to closely monitor with basal Pc following the administration of a loading dose, particularly in patients with renal failure.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2025 Camila Cabrera Díaz, Claudio Gonzalez Muñoz, Giannina Izquierdo Copiz