Abstract
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is an abnormal development of the components of the pediatric hip joint. Various screening programs are used, including physical examination, ultrasound, pelvic X-ray, or a combination of them.
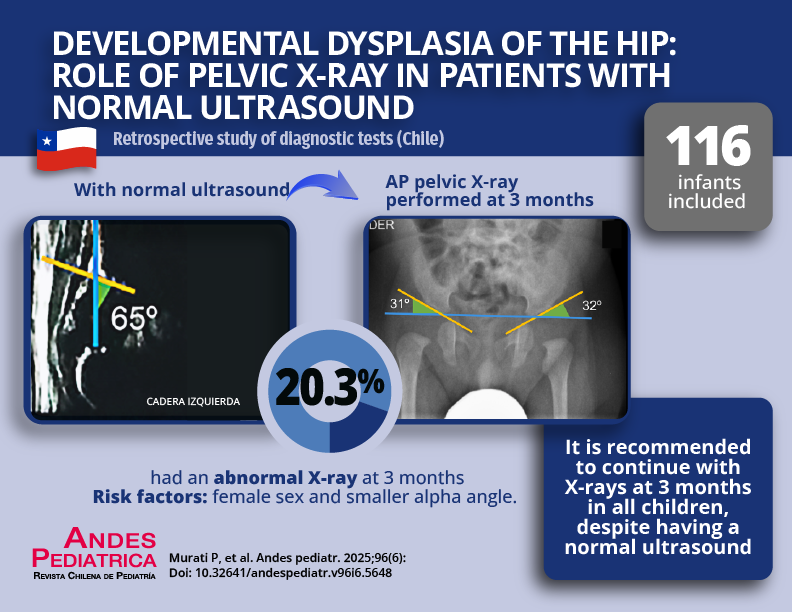
Objective: To evaluate the risk of abnormal findings on pelvic X-ray in infants with a normal early hip ultrasound.
Patients and Method: Retrospective diagnostic test study. Infants born between 2018 and 2021 with at least one risk factor for DDH were included. All patients had a normal hip ultrasound performed between the 2nd and 12th week of life and a pelvic X-ray obtained at or after 3 months of age. Demographic data, risk factors, ultrasound results (alpha angle according to Graf classification), and radiographic findings (acetabular index at 3 months) were collected. Data were analyzed to identify factors associated with abnormal radiographic findings.
Results: A total of 232 hips from 116 infants were included. Of these, 55.2% (n = 128) were male. At 3 months, 20.3% of the hips showed an abnormal pelvic X-ray. The main risk factors for this condition were a smaller alpha angle and female sex. An alpha angle < 65 degrees was associated with an odds ratio (OR) of 5.8 (95% CI: 2.0–11.6) for presenting an abnormal X-ray.
Conclusion: Infants with a normal ultrasound before 3 months of age with an alpha angle < 65° are at high risk of an abnormal pelvic X-ray; therefore, follow-up is recommended.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista Chilena de Pediatría